Understanding Torn Meniscus Recovery: Torn Meniscus Recovery Time
A torn meniscus is a common injury that can occur in the knee. The meniscus is a C-shaped piece of cartilage that acts as a shock absorber between the thighbone (femur) and shinbone (tibia). When the meniscus tears, it can cause pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the knee.
Types of Meniscus Tears
Meniscus tears are classified based on their location and severity.
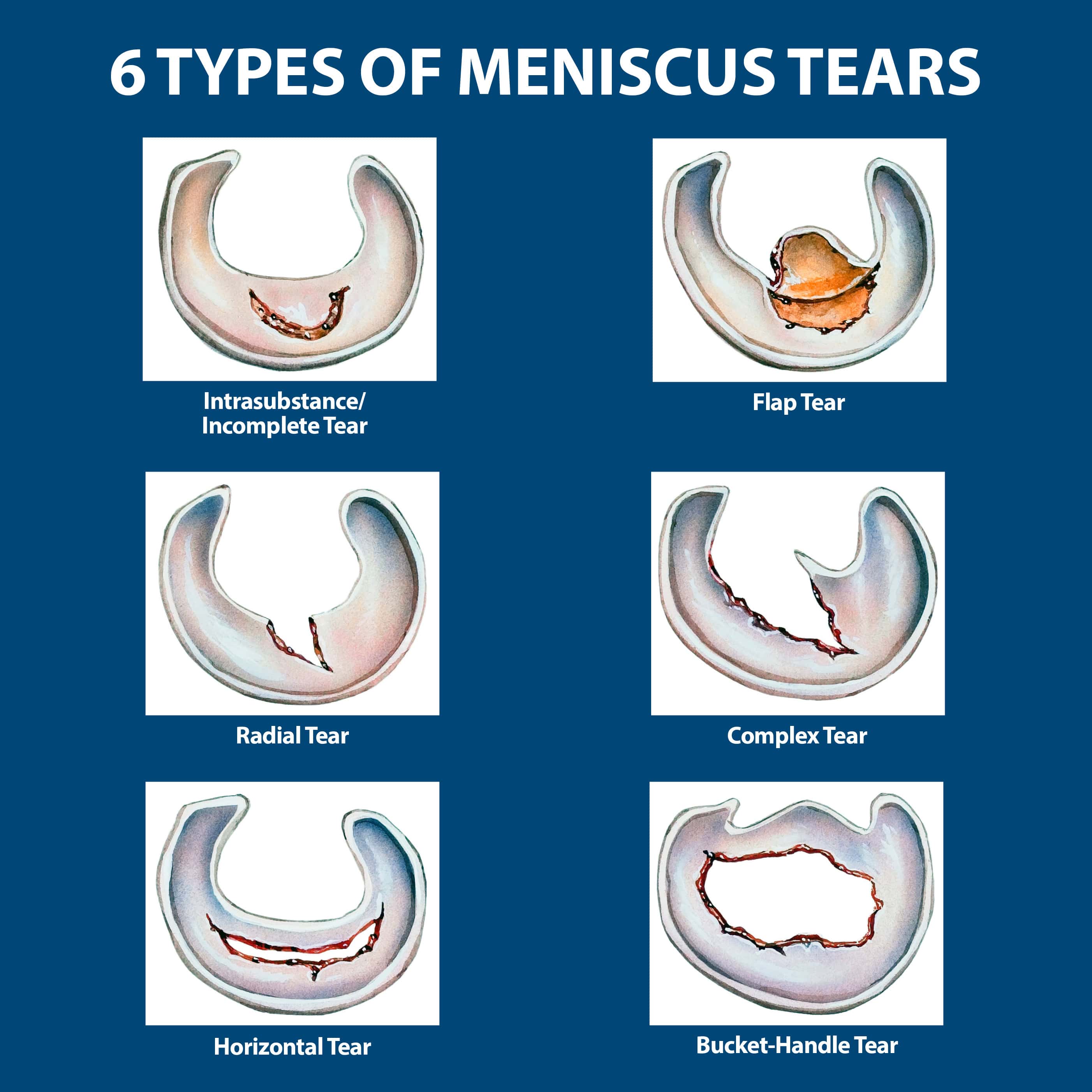
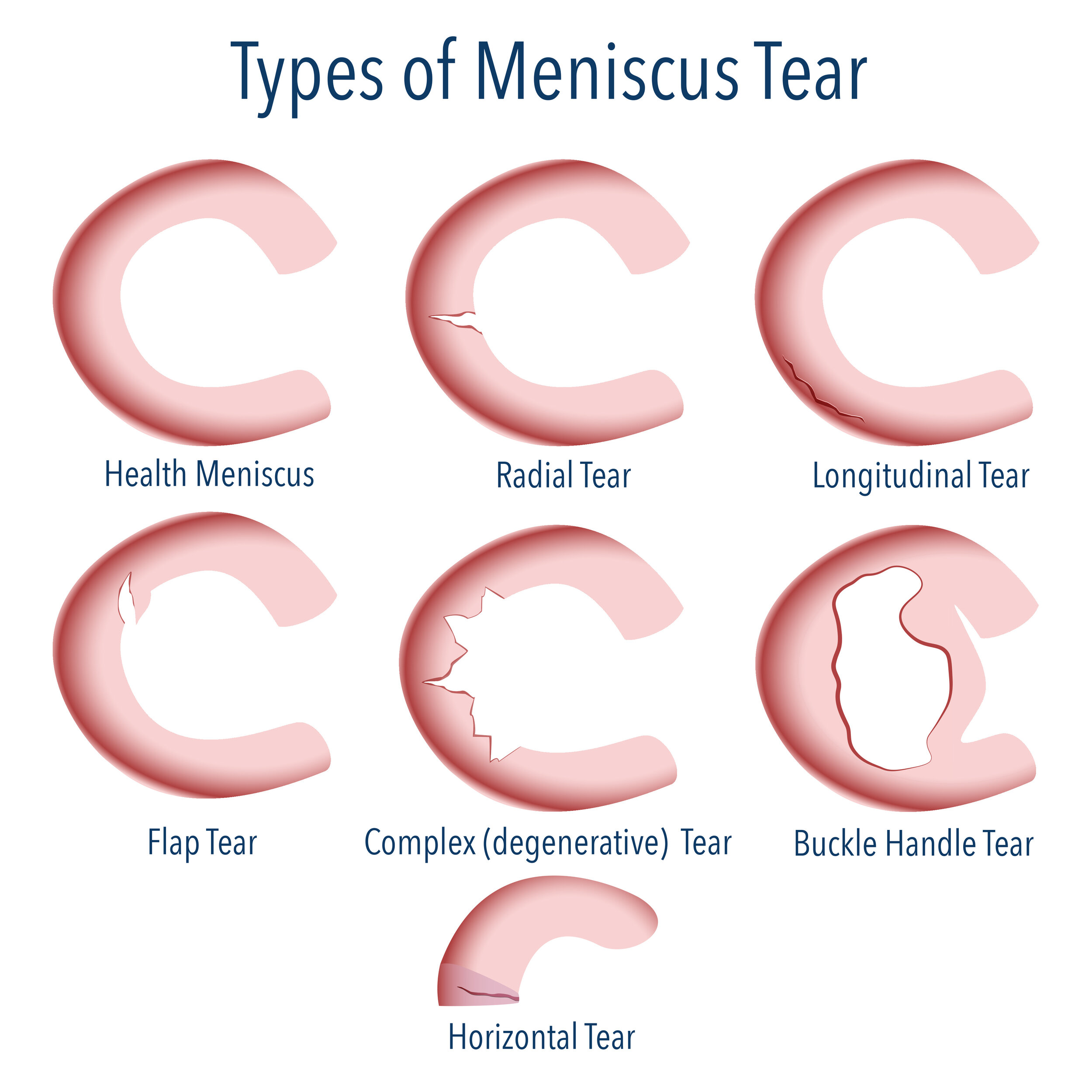
- Horizontal Tear: This type of tear runs across the width of the meniscus. It is often caused by a sudden twisting or impact injury.
- Vertical Tear: This type of tear runs up and down the length of the meniscus. It can be caused by a sudden twisting or impact injury, or by repetitive wear and tear.
- Radial Tear: This type of tear is a combination of horizontal and vertical tears. It is often caused by a sudden twisting or impact injury.
- Degenerative Tear: This type of tear is caused by wear and tear on the meniscus over time. It is often seen in older adults.
The severity of a meniscus tear can range from a small, partial tear to a large, complete tear.
Factors Influencing Recovery Time
Several factors can influence the recovery time for a torn meniscus, including:
- Age: Younger individuals tend to heal faster than older individuals.
- Activity Level: Individuals who are more active tend to have a longer recovery time than those who are less active.
- Tear Location: Tears in the outer part of the meniscus tend to heal better than tears in the inner part.
- Treatment: The type of treatment received can also affect recovery time.
Recovery Process
The recovery process for a torn meniscus typically involves several stages:
- Initial Stage: This stage involves reducing pain and swelling. This may involve rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) therapy.
- Rehabilitation Stage: This stage involves gradually increasing the range of motion and strength of the knee. This may involve physical therapy exercises.
- Return to Activity Stage: This stage involves gradually returning to activities as tolerated. This may involve a gradual increase in the intensity and duration of exercise.
The recovery time for a torn meniscus can vary depending on the severity of the tear and other factors. It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and to participate in physical therapy as prescribed.
Treatment Options for Torn Meniscus
The treatment approach for a torn meniscus depends on several factors, including the location and severity of the tear, the patient’s age, activity level, and overall health. The two primary treatment options are non-surgical and surgical.
Non-Surgical Treatment
Non-surgical treatment is often the first line of approach for a torn meniscus. This involves managing the symptoms and allowing the tear to heal naturally. It typically includes:
- Rest: Avoiding activities that aggravate the knee joint.
- Ice: Applying ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
- Compression: Using a bandage or brace to reduce swelling.
- Elevation: Keeping the leg elevated above the heart to minimize swelling.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Using medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen to manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Performing exercises to strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee, improve range of motion, and enhance stability.
Non-surgical treatment is usually successful for minor tears, especially in younger individuals. However, if the tear is significant or causes persistent pain and instability, surgery may be necessary.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is considered when non-surgical treatment fails to alleviate symptoms or when the tear is severe. There are two main surgical procedures used for torn meniscus:
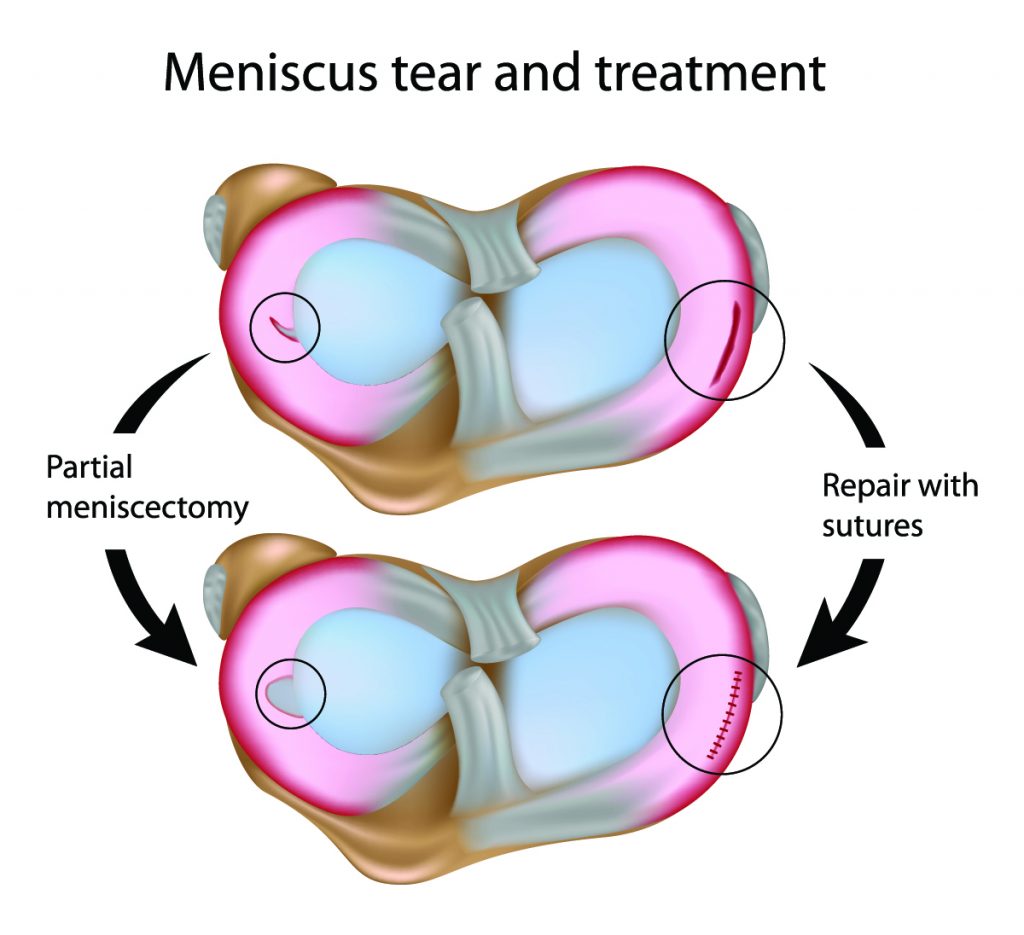
- Meniscectomy: This procedure involves removing the damaged portion of the meniscus. It is often used for tears that are located in the outer portion of the meniscus, known as the peripheral zone. The procedure is usually performed arthroscopically, which involves making small incisions and inserting a camera and surgical instruments into the knee joint.
- Meniscus repair: This procedure involves stitching the torn meniscus back together. It is typically used for tears that are located in the inner portion of the meniscus, known as the inner zone, where blood supply is better. Meniscus repair is often performed arthroscopically, and it involves using sutures or other techniques to reattach the torn fragments.
Benefits and Risks of Treatment Options
| Treatment Option | Benefits | Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Non-surgical treatment |
|
|
| Surgical treatment |
|
|
Different Surgical Procedures
The choice of surgical procedure depends on the location, size, and type of tear, as well as the patient’s age and activity level. Here are some examples of surgical procedures used for torn meniscus:
- Partial meniscectomy: This procedure involves removing only the damaged portion of the meniscus. It is often used for tears that are located in the outer portion of the meniscus.
- Total meniscectomy: This procedure involves removing the entire meniscus. It is typically reserved for cases where the meniscus is severely damaged and cannot be repaired.
- Meniscus repair with sutures: This procedure involves stitching the torn meniscus back together using sutures. It is often used for tears that are located in the inner portion of the meniscus, where blood supply is better.
- Meniscus repair with anchors: This procedure involves using small anchors to reattach the torn meniscus to the knee joint. It is often used for tears that are located in the outer portion of the meniscus, where the blood supply is poor.
Rehabilitation and Recovery After Treatment
Recovering from a torn meniscus requires a dedicated rehabilitation program to restore function, strength, and stability to your knee. This program typically involves physical therapy exercises and activities, and it’s crucial to follow your physical therapist’s instructions diligently for optimal recovery.
Physical Therapy Exercises and Activities
A comprehensive rehabilitation program for a torn meniscus will typically involve a progressive series of exercises designed to:
- Reduce pain and swelling
- Improve range of motion
- Strengthen muscles around the knee
- Enhance proprioception (awareness of your knee’s position in space)
- Gradually return to functional activities
Your physical therapist will guide you through these exercises, adjusting the intensity and complexity as you progress. Here are some examples of common exercises:
- Range of motion exercises: These include gentle knee bending and straightening to regain flexibility.
- Strengthening exercises: These involve using resistance bands or weights to strengthen the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles.
- Proprioceptive exercises: These exercises, such as balancing on one leg or performing agility drills, help improve coordination and stability.
- Functional exercises: As you progress, you’ll start performing more functional activities, such as walking, jogging, and stair climbing.
Importance of Following the Prescribed Rehabilitation Plan, Torn meniscus recovery time
Following your rehabilitation plan is essential for a successful recovery. This means attending physical therapy sessions regularly, performing your exercises as instructed, and gradually increasing the intensity and duration of your activities.
- Faster recovery: Adhering to your rehabilitation plan can help you recover more quickly and return to your desired activities sooner.
- Reduced risk of re-injury: Proper rehabilitation strengthens the muscles and ligaments surrounding your knee, reducing the risk of re-injury.
- Improved long-term outcomes: Following a structured rehabilitation program can help you regain full function and minimize long-term pain and limitations.
Managing Pain and Swelling During Recovery
Managing pain and swelling is crucial for a comfortable recovery. Here are some tips:
- Rest: Avoid activities that aggravate your knee.
- Ice: Apply ice to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
- Compression: Use a compression bandage to help reduce swelling.
- Elevation: Keep your leg elevated above your heart whenever possible.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage pain and inflammation.
It’s important to note that these tips are general guidelines. Always consult with your doctor or physical therapist for specific advice on managing your pain and swelling.
Torn meniscus recovery time – The recovery time for a torn meniscus can vary significantly depending on the severity of the tear and the chosen treatment method. A recent example of this is the jj mccarthy knee injury , where the Michigan Wolverines quarterback sustained a torn meniscus, requiring surgery and subsequent rehabilitation.
While some meniscus tears can heal with conservative management, others may require surgical intervention, potentially extending the recovery period.
The recovery time for a torn meniscus can vary significantly depending on the severity of the tear, the individual’s age and activity level, and the chosen treatment method. A torn meniscus occurs when the cartilage that cushions the knee joint is damaged, often due to a twisting or impact injury.
Non-surgical treatment options may involve rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), while surgical repair or removal of the damaged tissue may be necessary in more severe cases. Regardless of the treatment approach, a comprehensive rehabilitation program is essential to restore joint stability, strength, and range of motion, ultimately impacting the overall recovery time.
